Well it's hardly a birthday celebration! But certainly a time to reflect and assess myself and the achievements of PudendalNerve.com.au. The total visits in 12 months total an astounding 21,500 and the search terms are a clear indication that still, so little is understood of Pudendal Neuralgia worldwide.
The first note must be of thanks and of course, has to go to my husband Theo. Without Theo's daily help this site simply wouldn't be up and running.... neither would I!
Second note worthy thank you, and certainly something that can be celebrated, has to be the beautiful connections I've made in the past year. I've met the most inspiring, energising, kind, compassionate people, whether practitioners, therapists, chronic pain sufferers, or people attached to the pain system, you have been my encouragement and empathy. Your pain and/or knowledge inspire me to continue and get to the bottom of this dreaded pain issue (in the hope of resolving it not only for me but for all of us!), and/or try to voice my improvements for an ignorant WorkCover system.
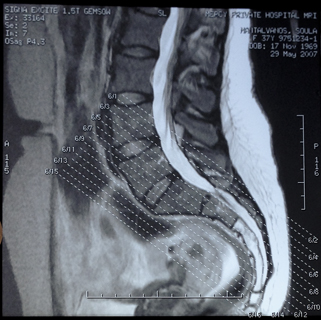
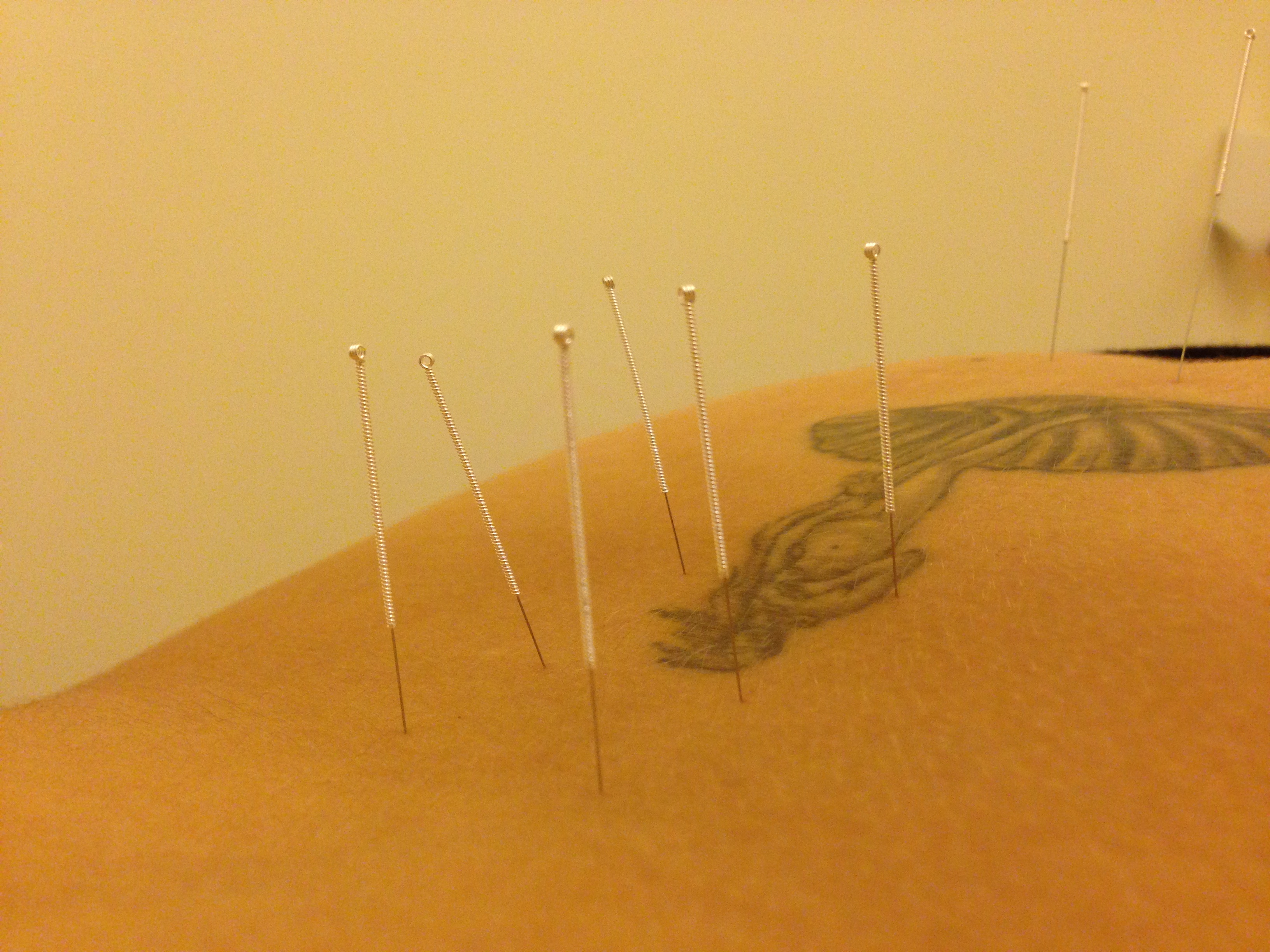
As far as my personal 1st year status goes, I definitely have 'progress' to celebrate; I'm running on Nerve block no. 3, refreshing my pelvis as required with a newly installed bidet, taking minimal amounts of Endep, in much less pain but still much limited with capacity and in need of daily help. Although I still need regular massage, I'm able to work a little from an accommodating home setup, thinking a lot more, delegating-delegating-delegating and finally, but not least, have taken a plunge into the wonderful world of Chinese Medicine which I believe may finally be able to reach my pain. Stay tuned for another update on that soon.
(image) Nerve Block Cake & Candle
To sum up, here are some stats that may be of interest to my subscribers and visitors (and my very loyal spies!).